
LinkedIn Temporarily Deindexed from Google via @MattGSouthern
LinkedIn found itself deindexed from Google search results on Wednesday, which may or may not have occurred due to an error on their part.
The telltale sign of an entire domain being deindexed from Google is performing a “site:” search and seeing zero results.
That was exactly the case with LinkedIn earlier today:
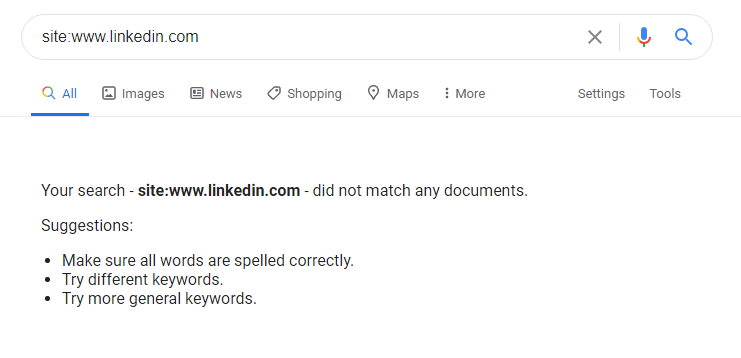

There were no results for LinkedIn in Google from early morning to mid afternoon on Wednesday – roughly 10 hours in total.
There’s no doubt this had a significant impact on LinkedIn’s traffic for the day, but the site itself was still accessible.
Users could still visit LinkedIn by navigating to the domain directly, or by clicking on links elsewhere on the web.
To be clear – the site was not down, it was just de-indexed from Google.
How Did This Happen?
The question of the day is how did this end up happening in the first place?
Neither LinkedIn or Google have officially commented on the subject at the time of this writing.
However, there are a couple of possible explanations.
LinkedIn May Have Removed HTTP Version of Site
John Mueller published a tweet this morning which may have been indirectly aimed at LinkedIn.
PSA: Removing the “http://” version of your site will remove all variations (http/https/www/non-www). Don’t use the removal tools for canonicalization.https://t.co/yTfRzWZGtd
— 🍌 John 🍌 (@JohnMu) May 6, 2020
It’s possible LinkedIn inadvertently removed itself from Google’s index by removing the HTTP version of its site in Search Console.
If that’s the case, which has not been confirmed, LinkedIn may have done so in an effort to canonicalize the HTTPS version of its site.
Mueller explicitly states: “Don’t use the removal tools for canonicalization.”
That’s one possibility. Here’s another potential explanation.
LinkedIn Disallowed Crawling Via Robots.txt?
According to evidence found while LinkedIn was de-indexed, it’s apparent Google’s crawlers were blocked with a robots.txt directive.
Pretty amazing that @LinkedIn has blocked themselves from Google.
Wonder if they also removed themselves via GSC to get this much of a clean break!
h/t @IanLurie pic.twitter.com/r02yH1qS5R
— lorenbaker (@lorenbaker) May 6, 2020
Blocking Google’s crawlers is a sure way to get de-indexed as well. However, the impact usually isn’t as immediate as it was in LinkedIn’s case.
As stated by Loren Baker in the tweet above, this much of a “clean break” from Google’s index is more likely to be related to a Google Search Console removal.
Related: 9 Ways to Deindex Pages from Google
LinkedIn is Back in Google Search Results
Whatever the issue may have been, it has since been corrected as LinkedIn has returned to Google’s search results.
If nothing else, let this be a lesson that even some of the web’s biggest sites make mistakes from time to time.
This can also serve as a lesson that Google does not fix mistakes on its own.
Never assume that Google is smart enough to detect these things and fix them before they turn into a major issue.
Lesson learned: never assume Google is smart enough to do anything.
— Dustin Woodard (@webconnoisseur) May 6, 2020
Rest assured the SEO community will not let LinkedIn live this one down any time soon.
I’ll wager that, for years to come, we’ll be referencing the time LinkedIn de-indexed itself from Google.
Related: How Search Engines Crawl & Index





